Definition of Palindromic Rheumatism
Palindromic Rheumatism is a rare autoimmune condition characterized by recurring episodes of joint pain, swelling, and inflammation. It is often considered a precursor to rheumatoid arthritis. The term “palindromic” refers to the episodic nature of the condition, where symptoms come and go in an unpredictable manner. These episodes can last for hours or days before resolving completely, with no lasting damage to the joints. Palindromic Rheumatism primarily affects the small joints such as those in the hands and feet, but it can also involve larger joints like the knees or shoulders. While the exact cause is unknown, it is believed that genetic factors and environmental triggers play a role in its development.
Definition of Palindromic Rheumatism as an autoimmune condition
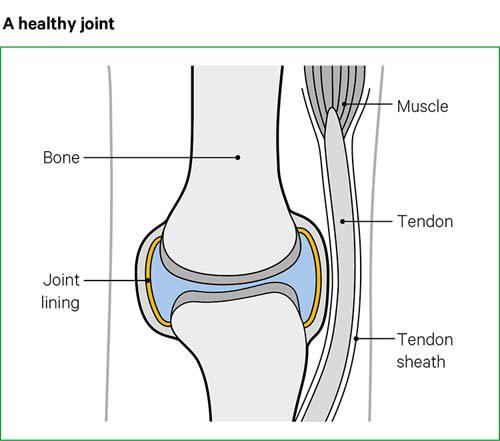
Palindromic Rheumatism is classified as an autoimmune condition, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In this case, the immune system targets the joints, leading to episodes of pain, swelling, and inflammation. The exact cause of Palindromic Rheumatism is still unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers. Unlike other forms of arthritis, Palindromic Rheumatism does not cause permanent joint damage during these episodes. However, if left untreated or unmanaged over time, it can progress into rheumatoid arthritis in some individuals. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are important for managing symptoms and preventing long-term complications.
Causes and Triggers of Palindromic Rheumatism
The exact cause of Palindromic Rheumatism is still unknown, but researchers believe that it is a result of a combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers. There seems to be a genetic predisposition to developing the condition, as it often runs in families. Environmental triggers such as infections, stress, hormonal changes, and certain medications have also been identified as potential factors that can trigger episodes of Palindromic Rheumatism. It is important to note that not all individuals with these risk factors will develop the condition, and there may be other unidentified factors at play. Further research is needed to fully understand the causes and triggers of Palindromic Rheumatism.
Common Symptoms of Palindromic Rheumatism
Palindromic Rheumatism is characterized by recurrent episodes of joint pain and swelling. The symptoms typically occur suddenly and can affect any joint in the body, although the most commonly affected joints are the fingers, wrists, and knees. During an episode, individuals may experience redness and warmth around the affected joint. These symptoms can last for a few hours to a few days before disappearing completely. One distinctive feature of Palindromic Rheumatism is that the symptoms come and go, with symptom-free periods in between episodes. This fluctuating pattern of symptoms can make it difficult to diagnose the condition early on. However, keeping track of these episodes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of Palindromic Rheumatism.
Common symptoms of joint pain and swelling
The most common symptoms of Palindromic Rheumatism are joint pain and swelling. These symptoms can occur suddenly and affect any joint in the body, although the fingers, wrists, and knees are often the most affected. During an episode, individuals may also experience redness and warmth around the affected joint. The duration of these symptoms can vary, lasting from a few hours to a few days before disappearing completely. It is important to note that Palindromic Rheumatism is characterized by its fluctuating pattern of symptoms, with periods of no symptoms in between episodes. This intermittent nature of the condition makes it challenging to diagnose early on but keeping track of these episodes can aid in accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Fluctuating Symptoms and their impact on daily life
The fluctuating nature of Palindromic Rheumatism symptoms can have a significant impact on daily life. The unpredictable episodes of joint pain and swelling can disrupt normal activities, making it difficult to plan and carry out daily tasks. During flare-ups, individuals may experience limitations in their range of motion and find it challenging to perform simple movements like gripping objects or walking comfortably. This can interfere with work, social activities, and overall quality of life. Additionally, the uncertainty of when the next episode will occur can cause anxiety and stress. It is important for individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism to develop coping strategies and seek support from healthcare professionals to manage these fluctuations effectively.
Diagnosing Palindromic Rheumatism

Diagnosing Palindromic Rheumatism can be challenging because of its episodic and unpredictable nature. Healthcare providers rely on specific diagnostic criteria to make an accurate diagnosis. These criteria include the presence of recurrent episodes of joint pain and swelling that resolve completely between attacks, as well as the absence of joint erosion or damage on imaging tests.
In addition to these criteria, healthcare providers may perform various tests and examinations to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Blood tests may be done to check for inflammation markers and antibodies associated with autoimmune diseases.
Effective diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management and treatment of Palindromic Rheumatism. If you suspect you have this condition, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in rheumatic diseases.
Diagnostic criteria used by healthcare providers
Healthcare providers rely on specific diagnostic criteria to accurately diagnose Palindromic Rheumatism. These criteria include the presence of recurrent episodes of joint pain and swelling that completely resolve between attacks. It is also important for healthcare professionals to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. To do this, they may perform various tests and examinations, including blood tests to check for inflammation markers and antibodies associated with autoimmune diseases. Imaging tests may also be done to assess joint erosion or damage.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment of Palindromic Rheumatism. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in rheumatic diseases is essential if you suspect you have this condition.
Tests and examinations for diagnosing Palindromic Rheumatism
To diagnose Palindromic Rheumatism, healthcare providers rely on specific tests and examinations. These help to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms and confirm the presence of this autoimmune condition. Blood tests are commonly used to check for inflammation markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). They may also look for antibodies associated with autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be performed to assess joint erosion or damage. Additionally, thorough physical examinations and patient history assessments are crucial in making an accurate diagnosis. Consulting with a rheumatologist is essential to receive proper testing and diagnosis for Palindromic Rheumatism.
Treatment Options for Palindromic Rheumatism

Treatment options for Palindromic Rheumatism focus on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Medications are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Biologic therapies may also be recommended in some cases. Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing symptoms. It is important for individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Medications and therapies for managing symptoms
Treatment options for Palindromic Rheumatism focus on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Medications are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Biologic therapies may also be recommended in some cases. Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing symptoms. It is important for individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Lifestyle changes and self-care techniques
In addition to medications and therapies, making certain lifestyle changes and incorporating self-care techniques can help individuals manage their symptoms of Palindromic Rheumatism. Regular exercise, such as gentle stretching or low-impact activities like swimming or yoga, can help improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or mindfulness meditation, may also be beneficial in reducing flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy diet that includes anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids and colorful fruits and vegetables, may help reduce inflammation in the body. It is important for individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism to listen to their bodies and pace themselves accordingly, avoiding overexertion or activities that may trigger symptoms.
Prognosis and Complications of Palindromic Rheumatism

Individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism have a varied prognosis, as the condition can differ from person to person. Some individuals may experience infrequent and mild episodes of symptoms, while others may have more frequent and severe flare-ups. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, many people with Palindromic Rheumatism are able to manage their symptoms effectively and maintain a good quality of life.
However, it’s important to note that Palindromic Rheumatism is considered a chronic condition and there is currently no cure. In some cases, it may progress to other forms of rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, prolonged inflammation in the joints can lead to joint damage over time.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring the progression of the disease and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. By working closely with healthcare professionals and following recommended treatments, individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism can optimize their long-term outcomes and minimize potential complications.
Long-term outlook for individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism
The long-term outlook for individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism can vary depending on the individual and the severity of their symptoms. While there is currently no cure for the condition, with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, many people are able to effectively manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring disease progression and adjusting treatment plans as needed. By closely collaborating with healthcare professionals and adhering to recommended treatments, individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism can optimize their long-term outcomes and minimize potential complications.
It’s important to note that in some cases, Palindromic Rheumatism may progress to other forms of rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, prolonged inflammation in the joints can lead to joint damage over time. Therefore, early detection and appropriate management are essential to minimize these risks.
Possible complications and associated conditions
While Palindromic Rheumatism is generally considered a milder form of rheumatic disease, there are potential complications and associated conditions that individuals may experience. Prolonged inflammation in the joints can lead to joint damage over time, which may result in chronic pain and limited mobility. In some cases, Palindromic Rheumatism can progress to other forms of rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism may be at an increased risk for developing cardiovascular problems due to systemic inflammation. It is important for individuals with this condition to regularly monitor their symptoms and work closely with their healthcare providers to minimize the risk of complications and manage any associated conditions effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Palindromic Rheumatism is a unique autoimmune condition characterized by recurring episodes of joint pain and swelling. It is important to recognize the fluctuating nature of symptoms, as they can greatly impact an individual’s daily life. While there is no cure for Palindromic Rheumatism, prompt diagnosis and appropriate management can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment options include medications to reduce inflammation and manage pain, as well as lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise. Regular monitoring of symptoms is crucial in order to identify any progression or development of associated conditions. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with Palindromic Rheumatism can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Resources for further information and support:
- Arthritis Foundation: www.arthritis.org
- American College of Rheumatology: www.rheumatology.org
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases: www.niams.nih.gov
Summary of Palindromic Rheumatism symptoms and management
Palindromic Rheumatism is characterized by recurring episodes of joint pain and swelling. The symptoms fluctuate, impacting daily life. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Treatment options include medications to reduce inflammation and manage pain, as well as lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise. Monitoring symptoms is important for identifying any progression or development of associated conditions. While there is no cure for Palindromic Rheumatism, working closely with healthcare providers can effectively manage the condition and improve quality of life.
Resources for further information and support:
– Arthritis Foundation: www.arthritis.org
– American College of Rheumatology: www.rheumatology.org
– National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases: www.niams.nih.gov
Resources for further information and support
If you are looking for more information or support regarding Palindromic Rheumatism, there are several resources available to help you. The Arthritis Foundation (www.arthritis.org) is a great place to start, offering comprehensive information on various types of arthritis and related conditions. The American College of Rheumatology (www.rheumatology.org) is another valuable resource that provides educational materials and access to healthcare professionals specializing in rheumatic diseases. Additionally, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (www.niams.nih.gov) offers research updates, treatment options, and patient resources. These organizations can provide further guidance and support as you navigate your journey with Palindromic Rheumatism.




